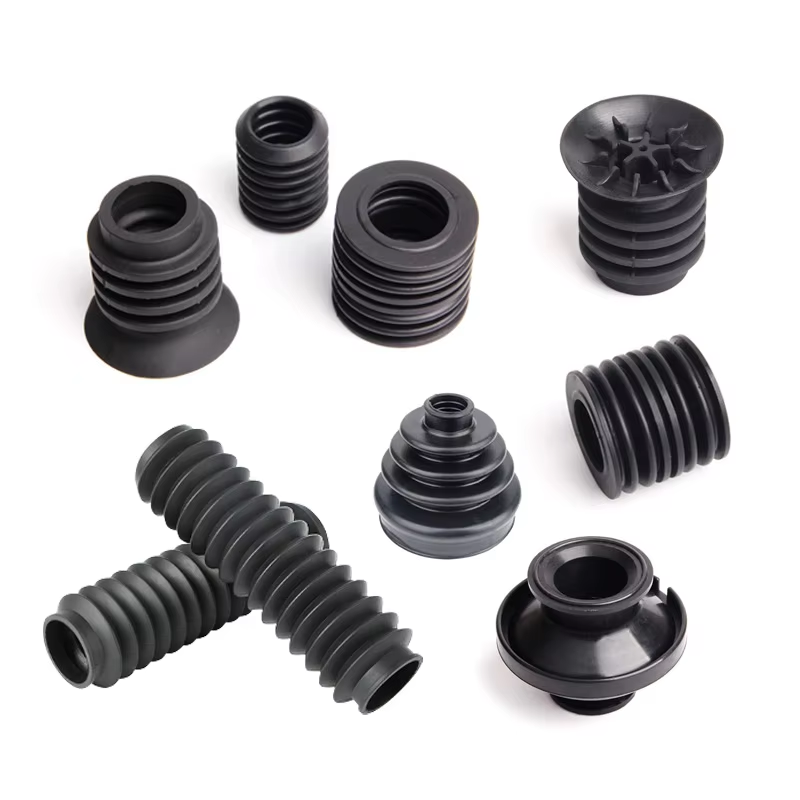
Understanding Your Project's Rubber Gasket Requirements
It all starts by identifying what you need as an end user — which is to match your needs with the optimum rubber gasket type that you can find! Silicone is best suited for high-temperature applications of 450°F (232°C) and nitrile is resistant to oil, gas and fuel. Mechanical stress must also be considered—vibrating dynamic systems need a material possessing both flexibility and low compression set, such as EPDM.
Regulatory compliance narrows options further. FDA-approved elastomers are essential for food processing, while ASTM D2000-certified grades ensure durability in industrial hydraulics. Industry-specific protocols like ISO 9001 for aerospace seals add another layer of scrutiny. Alignment between these factors prevents premature failure and costly downtime.
Collaborate with material specialists during the design phase. A thorough audit of environmental conditions, load cycles, and maintenance constraints reduces inefficiencies. For automotive weatherstripping or pharmaceutical cleanroom seals, precise requirements mapping directly impacts sealing longevity and system reliability.
Critical Material Properties in Rubber Gasket Selection
To ensure sealing effectiveness across industrial applications, focus on these four key performance factors:
Temperature Resistance and Thermal Stability
Rubber gaskets must withstand temperatures from cryogenic conditions (-65°F) to extreme heat (500°F). EPDM maintains flexibility at -40°F, while silicone resists brittle failure up to 450°F. Exceeding maximum service temperatures can lead to significant elasticity loss within 200 operational hours.
Chemical Compatibility with Operating Media
Material compatibility prevents swelling, cracking, or dissolution—a leading cause of 40% of gasket failures. EPDM works well with water-based coolants, while FKM (Viton®) resists hydrocarbon fuels and chlorinated acids. Always verify resistance charts for diluted vs. concentrated media exposure.
Pressure and Compression Set Tolerance
Hydraulic applications demand materials with ≤15% compression set after prolonged loading. High-performance fluorocarbon elastomers recover 98% of original thickness post-compression, outperforming standard nitrile by 40%.
Abrasion Resistance and Durometer Hardness
Surface wear accounts for 22% of dynamic seal replacements. Nitrile (70A durometer) balances pliability and wear resistance for rotating shafts. Polyurethane gaskets in slurry pumps offer 30% longer service life than silicone due to superior tensile strength.
Industry Standards for Rubber Gasket Compliance
Over 80% of sealing failures stem from deviations from material or testing protocols. Regulatory frameworks ensure material safety, pressure integrity, and environmental risk mitigation.
ASTM and FDA Certification Requirements
FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 standards are mandatory for food and pharmaceutical applications. ASTM D2000 classifications specify properties like tensile strength and heat resistance. Aerospace and military applications often require additional certifications like SAE AS1933.
Industry-Specific Pressure Testing Protocols
ASME BPVC Section VIII mandates hydrostatic testing at 1.5x operating pressure for boiler gaskets, while API 6A requires gas tests for oilfield equipment. Automotive coolant seals undergo ISO 16525-2 validation with 1,000-hour cyclic exposure.
Application-Specific Rubber Gasket Material Selection
A 2023 study found 63% of sealing failures result from incompatible material selection. Here are three top-performing elastomers:
EPDM for Automotive Weather Sealing
EPDM excels in automotive environments with its -58°F to 302°F range and ozone resistance. It maintains 88% compression recovery after repeated use, ideal for window seals and trunk gaskets.
Silicone for High-Temperature Industrial Processes
Silicone withstands 450°F while retaining flexibility—a 40% improvement over fluorocarbon alternatives. It’s widely used in aerospace and sterilization systems due to its UL 94 V-0 flame resistance.
Nitrile for Oil and Fuel Resistance
Nitrile demonstrates 98% compatibility with petroleum-based fluids, making it ideal for hydraulic systems. Automotive studies show it reduces diesel permeation by 73% compared to EPDM.
Optimizing Rubber Gasket Performance Through Installation
42% of gasket failures stem from improper installation. Follow these critical steps for optimal performance:
Surface Preparation Best Practices
Remove contaminants with non-abrasive brushes—even 0.1 mm of debris can cause uneven compression. Verify flatness with a straightedge; surfaces exceeding 0.05 mm/mm warpage need machining.
Torque Specifications and Load Distribution
Use a star-pattern tightening sequence at 30%, 60%, and 100% of the manufacturer’s torque specification. For EPDM gaskets, final torque typically ranges between 25–35 N·m. Calibrated torque wrenches are essential—a 10% deviation increases leakage risk by 27%.
Maintenance Schedule for Long-Term Sealing Integrity
Inspect static seals every 3–6 months and dynamic seals monthly. Key indicators include:
- Compression set: >15% permanent deformation
- Surface cracking: Depth exceeding 25% of thickness
- Chemical swelling: Volume increase >10%
Replace gaskets immediately if degradation thresholds are breached. For critical processes, integrate ultrasonic leak detection into annual maintenance protocols.
FAQ
What is the best material for high-temperature applications?
Silicone is the best material for high-temperature applications, retaining flexibility and resisting heat up to 450°F.
Which gasket material offers resistance to oil and fuel?
Nitrile is ideal for oil and fuel resistance, demonstrating 98% compatibility with petroleum-based fluids.
How often should gaskets be inspected for maintenance?
Static seals should be inspected every 3-6 months and dynamic seals should be checked monthly.
What certifications are important for food and pharmaceutical applications?
The FDA 21 CFR 177.2600 standards are necessary for food and pharmaceutical applications to ensure safety and compliance.

 EN
EN