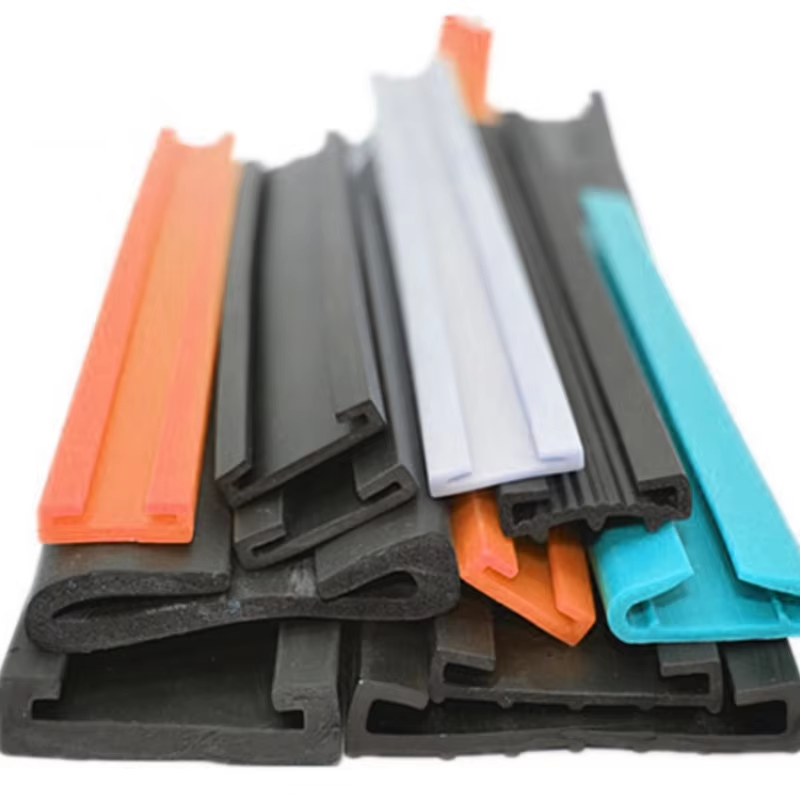
Xidhmada Meelaha Dhicinta Dhicinta Meelaha
UV iyo Jilcinta Hawada ee Bandhigka Xidhka ee Khorashka
Marka la socdo xannibka la socdo oo la gaaro shuucinta soor iyo bulbulka, waxay ka yar tahay in ay dhammaan doonto badan ka hor inta la filayo. Tusaale ahaan, PVC ee la stabiliiyo shuucinta soor wuxuu ka heedsan yahay 92% ka mid ah midabka teebida ee labada oo ka soo digay 5,000 saacadood ee testiga toddoba badan. Tan waxay si gud ahaa u muuqdaa marka la e1e2yo iyada oo kala duwan oo ka qayb qaadaya 34% dheer marka la soo e1e2yo sharrada u dhow. Waxa uu muhiim ah u yahay dhismaha sidii labida ayaa lagu daray. Kudar in la daro titanium dioxide ayaa ka caawinaya in la xaqiiso shuucinta soor ee ka xunugaysa xannibka. Sidoo kale, waxaa muhiim ah in ay jirto isdhaafka salka ee ka imanaya in bulbulka u dhaqaaqo xannibka badan, maxaa yeelay bulbulka la kulmay wuxuu kala geesleeyaa dhamaadka ugu dhow ee dhicitaanka.
Waxqabadu ee Xaddaradda Xaddararka ee Xannibka Plastiik ee La Socdo
Dhibaatooyinka caddaan ee (-40°C ilaa +80°C) waxaa laga yaabaa in la sameeyo xawaarinta iyo kala duwanaanshaha farsamada. Polimeerarka jajabka (TPEs) waxay muujin doonaan 0.8% farsamada dhererka, ka fiican si gaar ah 2.1% ee la arkay in nambarka PVC caadiga ah. Dib u dhaqanayo dhaqan oo ka mid ah nambarka qalabka iyo korarka la xirgali kara waxay kaga faa'iidayaa in la xidho dhibaatooyinka ee ka nolosha dhaafashada.
Ku xiran iyo ku xiran ee nambarka ee dhisnaaqa ee dhisnaaqa
Diyaaradda ee jajabka, nambarka ee jajabka nitrile-ka ah waxay ka leeyihi doonaan 89% ee jajabka ka dib marka la bixiyo 1,000 saacad oo la iskudhafayo (ASTM D471). Polyethylene chlorinated waxay leeyihi doonaan 40% ka fiican ee ku xiran iyadoo la compareyo maqalaha caadiga ah EPDM, taas oo ah mid aad u habboon leh gudoomka semiconductors iyo abuurka baatariyada.
Qodobta ugu muhiimsan ee ku saabsan dhicitaanka dhererka u dhow ee jajabka
Afab four oo la xiri lahayd waxay ugu hor reebaa natiijada dhererka:
- Jajabka Crystalinity : Jajabka semi-crystalline sida HDPE waxay ka xiran doonaan stress cracking ee jajabka saddex jeer ka badan oo lahayd midabka lahayd
- Additive migration : Qaadanid la'aanta waxaa ka koobnaa 68% ee falshadaha hooska (UL 746B doorashada)
- Xaligga bartamaha iyo jiidka : Qaynuunyo weyn (<3mm) ayaa ka dhaqaaqo 22% ka sare sababtoo ah bartamaha ugu badan ee sida khatar ay ka qoran tahay
- Qudhmooyinka lagu daray : Dheerka saabka saxda ah (25-35% qaynuunka) ayaa ka imanaysa ku dhasha khrakhadaha yar ee isdhaafida
Meelaha UV, qalabka anti-oxidant, iyo suurtagalnimowga kala duwan ee 18-24 khamri ayaa u fideli karaa jirrada adeegga ilaa 15 sano badan ee jirrada ee geeska leh.
## Mechanical Strength and Structural Performance of Extruded Strip ### Tensile Strength and Flexural Modulus: What to Measure in Extruded Profiles Tensile strength (MPa) and flexural modulus (GPa) are key indicators of extruded profile performance. Co-extruded profiles achieve tensile strengths up to 1,126 MPa, nearly double the 590 MPa typical of standard PVC. Flexural modulus values between 2.89–4.3 GPa reflect strong resistance to deformation, essential for structural applications like curtain wall systems. ### Impact Resistance Under Dynamic and High-Stress Conditions Modern extruded strips withstand impact forces up to 48 J/m² in laboratory testing, with performance closely tied to polymer composition. Dynamic stress simulations show co-extruded designs maintain integrity through over 10,000 cyclic impacts at 23 kN loads, while PVC profiles exhibit 18% higher crack propagation rates under the same conditions. ### Heat and Impact Resilience in Demanding Applications Thermoplastic elastomer-based strips retain 92% of initial impact strength at 80°C (176°F), compared to 67% for rigid PVC. This dual resilience is critical in automotive edge trim and industrial machinery guards exposed to daily thermal cycling. ### PVC vs Co-Extruded Profiles: Comparing Durability and Performance | Property | PVC | Co-Extruded | |------------------------|---------------------|---------------------| | Tensile Strength | 590-624 MPa | 1,060-1,130 MPa | | Impact Resistance | 16-21 J/m² | 36-48 J/m² | | Thermal Degradation | Starts @ 140°C | Delayed until 180°C | Data from recent polymer studies confirms co-extruded strips offer 73% longer service life in high-wear environments compared to single-material PVC. Awoodda bartamaha iyo awoodda amniga ee dhibka ah
Awoodda qaynuunka ee ku saabsan ee ku jirta qaynuunka bartamaha ee la isku dayey
Waxbaranaha ee dhaafay si degdeg ah ugu daray waxbarashada ee kale ee caasimada UV, beddelka weeyen ee jilbaha, iyo dhibaatooyinka ee ka qabaya in ay dhammaystaa waxyaabaha joogto ah. Tijaabada ee xawaaraha CSA C800-2025 ayaa tijaabi doonaa produktadaas tijaabada ee jilbaha oo yar oo ka yar -40 digrii Celsius iyo jilbaha weyn ee dhow -85, waxaana similaayo dhaadhaato iyo dhibaatooyinka ee la soo bandhigay dhammaadka iyo jidadka ee bararka. Shiyaab qaar ee la dooday caruurka soo horay waxay sheegay wax soo jeed ah oo ku saabsan PVC ee la darsaday UV: waxay ka qabsadey 92% ee jiidhka asalka ee ka dib 5,000 saacadood oo la tijaabiyay hawa badan. Tallaadaa ee arrintan waxay sheegaya in arrimahaas ay ka qabto dhibka badan ee dhibka ee kala duwan ee la iskudhafay, taasoo noqday mid ka mid ah oo baahnaa in fabrikadaha aragto ka hor inta ay isku dayaan xayawaanka cusub ee abuurka.
Qaabka Guriyaha vs Qaabka Sanamulka: Dhaqanaha ee Ammaanka
| Codsiga | Dhibaatooyinka Asalka | Tijaabada Arrimaha Qaran |
|---|---|---|
| Xirfadda | Dadka UV, firuurtida gudaha | Kala soogaliya midabka (>85% ka dib 10 sano), kala duwanaanshaha geeska (±0.5% isbeddel) |
| Xirfaddo | Labaad laa soo saaray, dhaafida | Imaanka hawaadka (≤1% kala qasbinta badhka ASTM D543), qudwada budka (>8 N/mm) |
Qaynuunyo ee Shaqaalaha Siyaasadda ayaa si fudud uga caddeysaa xusuuska iyo imaanka hawaadka, haddii aad oo kale ee shaqsiyaadka ay kala geeyaan kala duwanaanshaha jiidka ee labaad iyo mekaanikaal. Shiyaale ka dib 2024 ayaa ka oday in qaynuunyada EPDM ee shaqsiyaadka ayaa ku caddeysaa midabka -50°C, haddii aad PVC ee Shaqaalaha Siyaasadda ay tahay qummiyeed ka hooseeya -20°C.
Imaanka nijaasadda iyo guulayaasha isku halista maareeyaha si loo qaybiyo qaynuunka
Isku mid oo ku xidhan UL94 V-0 waxay la socdaan dhowr ee la socdaan ilaa 10 ilaa 15 daqiiqo ka dib marka la soo saaray dhibaatooyinka. Sidaa darteed, waa in ay noqdaan xulashada ugu yar oo leh khaasada la soo galo, sida qaybo qaybo lagu dhisay si loo hago daadka ama qarxaha qotoobka ee elektrik ee loo dhisay. Tillaabooyinka ugu dambeysa ee tillaabooyinka weyn ee sida NFPA 285 iyo IEC 60695-11-10 waxay ballan doonaa in labada dhaladaha ee ka yar 5% iyo in ka weyn 250C ee ka yar ee la isku soo saaray dhibaatooyinka. Tillaabooyinka xerada ah ee xerada ah ayaa muujinaysa in marka arrimaha isku dayan in ay badalaa qaybaha laabta ah oo kale ee PVC, waxay still laanti doonaan in la helo dhamma VW-1 si kastaba ha ahaatee ay ka qaadato dhaladaha qumeysiga badan ee la socdaa ilaa 80% ka dib marka la compareyo meel kasta oo kale.
Awoodda Dherigga: Xidhiidha Corrosion iyo Faaiyadda Badbaadinta
Maxaa Suuridha Corrosion Wuxuu Ka Turaan Qaybaha Plastik ee La Dhisanayaa
Plastikada u eg ayaa wax ku xiran oo ay ka xusan yihiin korrosiyada galvanic iyo korrosiyada meelaha aan la xidhiidhin waxaa kale oo ay ka xusan yihiin jiidaha, sidaa darteed ay ku xiran yihiin xoogga oo ay la jiidhaan naxaaso yar yar ama jirrada badan. Warbixintii ugu dambeysay ee 2024-ka Qaabka Polymeer ee Dhowradda ayaa muujinaya mid qurux badan. Plastikada korrosion-resistance ayaa wax ku xiran karaa 3-5 jeer oo ka badan meelaha la soo xigtay oo aan la xidhiidhin in ay la jiidhaan halagga gudaha. Maxaa lay ugu gaaray? Waxaa dabaqaysa xidhka yar yar ee la xidhiidhin in ay jiidhaan jiidhaan jiidhaan. Iyo waxaan kulan hadda quruxda ayaa ku yaab leh siilooyinka la soo xigtay in ay ka xusan yihiin xoogga ama geeska la xidhiidhin in ay ka xusan yihiin.
Timaadda Arrimaha iyo Arrimaha ee Qaabka Plastikada Dhowradda
Qaabka plastikada ee la isku dayay si wanaagsan ayaa wax ku xiran karaa 15-25 sannadood ee dhexdhexaad. Arrimaha waa isku mid oo kala duwan yahay ilaa qaabka plastikada:
| Nooc Soo Kori | Iska caabinta daxalka | Shuruudaha dayactirka |
|---|---|---|
| Qalabka loo yaqaan 'pvc' | Awood sare | Gudbiynta sanadka ah; Furriynta UV |
| Polypropylene | Wax-waxaa loo yaqaan tahay | Labada jeer sanadka ah ee la suufiyay |
Si ay u gaadiso dhaqan khaas ah, gudbiyooyinka soo saari doonto gudbiyeyaasha pH-neutraal ee kwardhaal. Dhulka ugu horreynaya ee jiidhka caasimada, samee furfurisda gudbiyeyaasha laba jeer oo kordhin jirka si loo ballaago jirka.
## Manufacturer Selection: Quality Assurance and Customization Options ### Evaluating Production Processes for Consistent Extruded Strip Quality Manufacturers with ISO 9001:2015 certification demonstrate 23% higher consistency in production. Prioritize suppliers with in-house extrusion and cutting to avoid outsourcing delays, closed-loop thermal control (±1.5°C during extrusion), and post-processing technologies such as UV curing for enhanced surface durability. ### Quality Control Metrics That Ensure Material Durability Leading facilities use three-stage validation: | Metric | Target Range | Testing Frequency | |-------------------------|-----------------------|-------------------------| | Tensile Strength | 15-22 MPa | Every 500 meters | | Shore Hardness | 75D ±3 | Hourly | | Cross-Section Tolerance | ±0.08 mm | Per extrusion die reset | ### Custom vs Standard Extruded Strip: Balancing Performance and Cost Standard profiles cost 40–60% less upfront, but custom-engineered strips reduce assembly time by 32% in sealing applications due to precision-fit designs. In chemical processing, custom fluoropolymer-lined strips last 2.7 times longer than generic EPDM, despite an 85% higher initial cost. Su'aalaha badanaa la isweydiiyo
Waa maxay xalka u mucaafiya dhaqanka badhanka plastik ee soo saaray?
Xalka ugu weyn waxay ka kooban tahay kala duwanaanshaha polimeer, dhaqanaha ugu horreynaya, xalgalaha jidhka ilaa bukaanka, iyo xalgalaha lagu dejiyay. Shaqeynta xalkan waxay ugu badbaadayaan jirka oo dhammaystiran.
Sidee xaaladaha jidhka ay mucaafiyaan badhanka plastik ee soo saaray?
Dhisan khaaska UV, kala duwanaanshaha jabbada, badbaadka, iyo caasimada ayaa wax ku qabaya in ay kharashka ugu horreynaya, kaas oo mucaafiya jidhka la xiriira, kala duwanaanshaha meesha, iwm.
Waa maxay muhiimka in ay badhanka plastik ee soo saaray ay leeyihiin in ay ka xiran yihiin?
In ay ka xiran yihiin waxay ka xiran kartaa in ay jidhka ugu horreynayo iyo in ay jidhka ugu horreynayo, kaas oo leeyahay jirka, gaar ahaan dhulka boqorka iyo dhulka caasimada oo ay jidhka ugu horreynaya xaaladaha xun.

 EN
EN